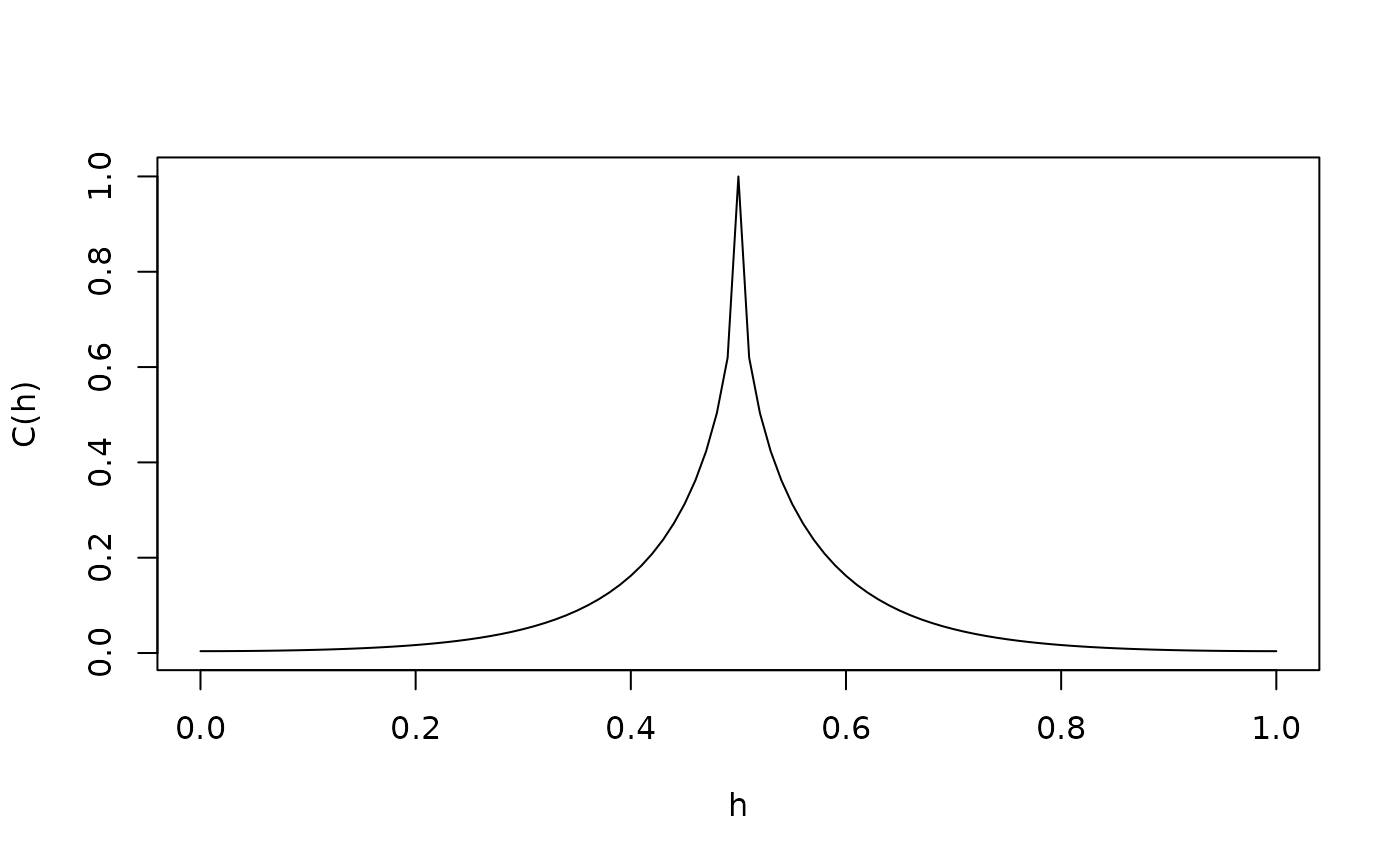
The 1d folded Matern covariance function
Source:R/covariance.functions.R
folded.matern.covariance.1d.Rdfolded.matern.covariance.1d evaluates the 1d
folded Matern covariance function over an interval \([0,L]\).
Usage
folded.matern.covariance.1d(
h,
m,
kappa,
nu,
sigma,
L = 1,
N = 10,
boundary = c("neumann", "dirichlet", "periodic")
)Arguments
- h, m
Vectors of arguments of the covariance function.
- kappa
Range parameter.
- nu
Shape parameter.
- sigma
Standard deviation.
- L
The upper bound of the interval \([0,L]\). By default,
L=1.- N
The truncation parameter.
- boundary
The boundary condition. The possible conditions are
"neumann"(default),"dirichlet"or"periodic".
Details
folded.matern.covariance.1d evaluates the 1d folded Matern
covariance function over an interval \([0,L]\) under different
boundary conditions. For periodic boundary conditions
$$C_{\mathcal{P}}(h,m) = \sum_{k=-\infty}^{\infty} (C(h-m+2kL),$$
for Neumann boundary conditions
$$C_{\mathcal{N}}(h,m) = \sum_{k=-\infty}^{\infty}
(C(h-m+2kL)+C(h+m+2kL)),$$
and for Dirichlet boundary conditions:
$$C_{\mathcal{D}}(h,m) = \sum_{k=-\infty}^{\infty}
(C(h-m+2kL)-C(h+m+2kL)),$$
where \(C(\cdot)\) is the Matern covariance function:
$$C(h) = \frac{\sigma^2}{2^{\nu-1}\Gamma(\nu)}(\kappa h)^\nu
K_\nu(\kappa h).$$
We consider the truncation: $$C_{{\mathcal{P}},N}(h,m) = \sum_{k=-N}^{N} C(h-m+2kL), C_{\mathcal{N},N}(h,m) = \sum_{k=-\infty}^{\infty} (C(h-m+2kL)+C(h+m+2kL)),$$ and $$C_{\mathcal{D},N}(h,m) = \sum_{k=-N}^{N} (C(h-m+2kL)-C(h+m+2kL)).$$