Covariance-based approximations of intrinsic fields
Source:R/intrinsic.R
intrinsic.matern.operators.Rdintrinsic.matern.operators is used for computing a
covariance-based rational SPDE approximation of intrinsic
fields on \(R^d\) defined through the SPDE
$$(-\Delta)^{\beta/2}(\kappa^2-\Delta)^{\alpha/2} (\tau u) = \mathcal{W}$$
Usage
intrinsic.matern.operators(
kappa,
tau,
alpha,
beta = 1,
G = NULL,
C = NULL,
d = NULL,
mesh = NULL,
graph = NULL,
loc_mesh = NULL,
m_alpha = 2,
m_beta = 2,
compute_higher_order = FALSE,
return_block_list = FALSE,
type_rational_approximation = c("brasil", "chebfun", "chebfunLB"),
fem_mesh_matrices = NULL,
scaling = NULL,
opts = NULL
)Arguments
- kappa
range parameter
- tau
precision parameter
- alpha
Smoothness parameter
- beta
Smoothness parameter
- G
The stiffness matrix of a finite element discretization of the domain of interest.
- C
The mass matrix of a finite element discretization of the domain of interest.
- d
The dimension of the domain.
- mesh
An inla mesh.
- graph
An optional
metric_graphobject. Replacesd,CandG.- loc_mesh
locations for the mesh for
d=1.- m_alpha
The order of the rational approximation for the Matérn part, which needs to be a positive integer. The default value is 2.
- m_beta
The order of the rational approximation for the intrinsic part, which needs to be a positive integer. The default value is 2.
- compute_higher_order
Logical. Should the higher order finite element matrices be computed?
- return_block_list
Logical. For
type = "covariance", should the block parts of the precision matrix be returned separately as a list?- type_rational_approximation
Which type of rational approximation should be used? The current types are "brasil", "chebfun" or "chebfunLB".
- fem_mesh_matrices
A list containing FEM-related matrices. The list should contain elements c0, g1, g2, g3, etc.
- scaling
scaling factor, see details.
- opts
options for numerical calulcation of the scaling, see details.
Value
intrinsic.matern.operators returns an object of
class "intrinsicCBrSPDEobj". This object is a list including the
following quantities:
- C
The mass lumped mass matrix.
- Ci
The inverse of
C.- GCi
The stiffness matrix G times
Ci- Q
The precision matrix.
- Q_list
A list containing the blocks required to assemble the precision matrix.
- alpha
The fractional power of the Matérn part of the operator.
- beta
The fractional power of the intrinsic part of the operator.
- kappa
Range parameter of the covariance function
- tau
Scale parameter of the covariance function.
- m_alpha
The order of the rational approximation for the Matérn part.
- m_beta
The order of the rational approximation for the intrinsic part.
- m
The total number of blocks in the precision matrix.
- n
The number of mesh nodes.
- d
The dimension of the domain.
- type_rational_approximation
String indicating the type of rational approximation.
- higher_order
Boolean indicating if higher order FEM-related matrices are computed.
- return_block_list
Boolean indicating if the precision matrix is returned as a list with the blocks.
- fem_mesh_matrices
A list containing the mass lumped mass matrix, the stiffness matrix and the higher-order FEM-related matrices.
- make_A
Use
make_A()to compute the projection matrix linking the field to observation locations.- variogram
A function to compute the variogram of the model at a specified node.
- A
Matrix that sums the components in the approximation to the mesh nodes.
- scaling
The scaling used in the intrinsic part of the model.
Details
The covariance operator
$$\tau^{-2}(-\Delta)^{\beta}(\kappa^2-\Delta)^{\alpha}$$
is approximated based on rational approximations of the two fractional
components. The Laplacians are equipped with homogeneous Neumann boundary
conditions. Unless supplied, the scaling is computed as the lowest positive eigenvalue of
sqrt(solve(c0))%*%g1%*%sqrt(solve(c0)). opts provides a list of options for the
numerical calculation of the scaling factor, which is done using Rspectra::eigs_sym.
See the help of that function for details.
Examples
if (requireNamespace("RSpectra", quietly = TRUE)) {
x <- seq(from = 0, to = 10, length.out = 201)
beta <- 1
alpha <- 1
kappa <- 1
op <- intrinsic.matern.operators(
kappa = kappa, tau = 1, alpha = alpha,
beta = beta, loc_mesh = x, d = 1
)
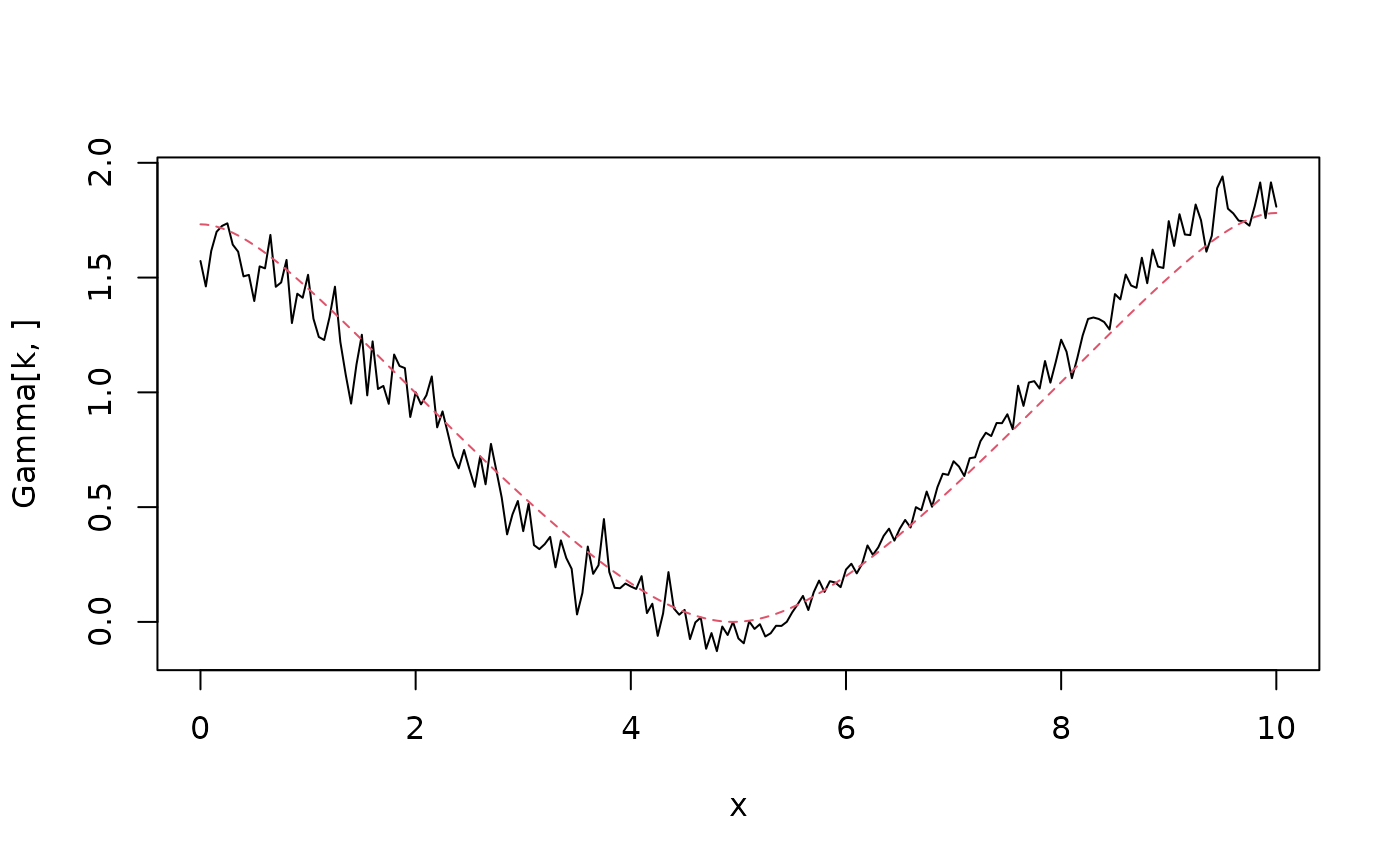
# Compute and plot the variogram of the model
Sigma <- op$A[,-1] %*% solve(op$Q[-1,-1], t(op$A[,-1]))
One <- rep(1, times = ncol(Sigma))
D <- diag(Sigma)
Gamma <- 0.5 * (One %*% t(D) + D %*% t(One) - 2 * Sigma)
k <- 100
plot(x, Gamma[k, ], type = "l")
lines(x,
variogram.intrinsic.spde(x[k], x, kappa, alpha, beta, L = 10, d = 1),
col = 2, lty = 2
)
}