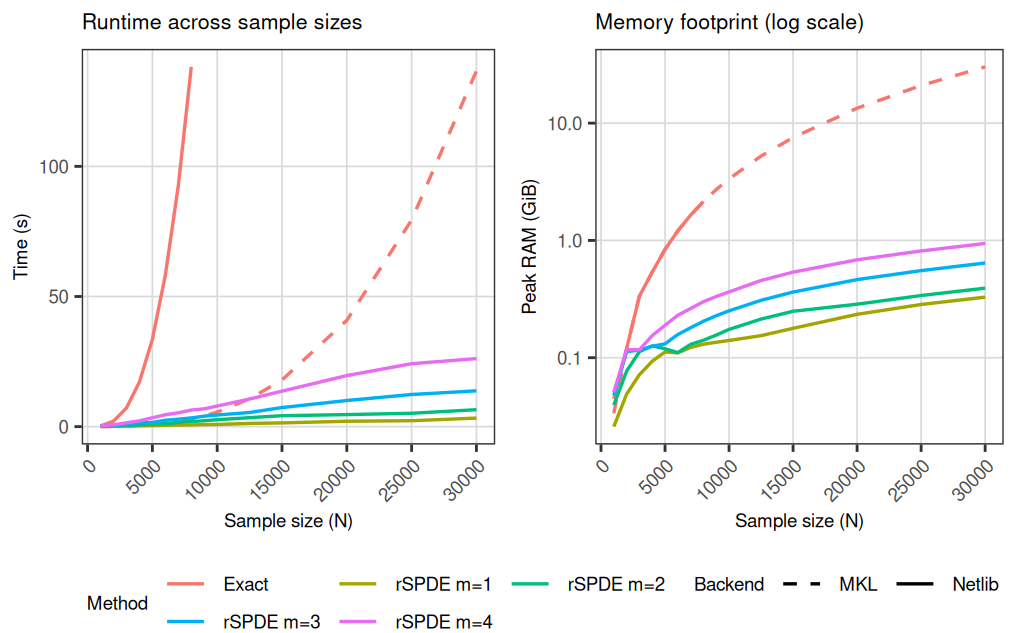
rSPDE vs exact Matern covariance: timing and memory
Source:vignettes/rspde_vs_exact.Rmd
rspde_vs_exact.Rmd
library(rSPDE)
library(fmesher)
library(Matrix)
library(ggplot2)
library(dplyr)
library(gridExtra)
library(gtable)
library(tidyr)Introduction
This vignette compares the computational cost of exact dense Matérn likelihood evaluation with the sparse rSPDE approximation. For the R-INLA implementation of rSPDE, see R-INLA implementation of the rational SPDE approach. For the inlabru implementation, see inlabru implementation of the rational SPDE approach. For a general introduction, see An introduction to the rSPDE package. For covariance-based and operator-based workflows, see Rational approximation with the rSPDE package and Operator-based rational approximation. For additional modeling examples, see Anisotropic models, Intrinsic models in the rSPDE package, Spatio-temporal models, and Rational approximations without finite element approximations.
rSPDE sparse approximation
rSPDE replaces dense covariance computations with sparse precision matrix computations by constructing a Gaussian Markov random field (GMRF) representation. The resulting linear algebra is substantially cheaper in both time and memory than dense covariance factorizations. The approximation order controls accuracy; the approximation error decreases exponentially fast with , so small orders often provide high accuracy at low computational cost.
Benchmark setup
We consider a Gaussian model
where
is a Mat'ern field on the unit square and the observations are taken at
random locations
.
We use
.
For each
,
we build a triangulation with fm_mesh_2d using
cutoff = 0.0025, construct the observation matrix with
fm_basis, and compare the cost of evaluating:
- the exact dense Mat'ern likelihood, based on the Cholesky factorization of the covariance matrix, and
- the rSPDE sparse log-likelihood for approximation orders .
For each , the rSPDE timing is averaged over 10 runs. When R is linked to FlexiBLAS and MKL or vecLib is available, we evaluate the exact model under Netlib (up to ) and under MKL/vecLib for all sample sizes, while running rSPDE under Netlib for all sample sizes. Otherwise, both exact and rSPDE timings use the base R BLAS.
Netlib BLAS is single-threaded, whereas MKL is multi-threaded. To keep the overall cost manageable, the exact Netlib evaluations are only computed up to , since dense Cholesky factorization becomes prohibitively expensive at larger in a single-threaded setting.
loglike_exact_chol <- function(y, Sigma_matern, sigma_e) {
S <- Sigma_matern
diag(S) <- diag(S) + sigma_e^2
chol_U <- tryCatch(chol(S), error = function(e) NULL)
if (is.null(chol_U)) {
return(-Inf)
}
log_det <- 2 * sum(log(diag(chol_U)))
z <- backsolve(chol_U, y, transpose = TRUE)
-0.5 * (length(y) * log(2 * pi) + log_det + sum(z^2))
}
has_flexiblas <- function() {
if (!requireNamespace("flexiblas", quietly = TRUE)) {
return(FALSE)
}
out <- try(flexiblas::flexiblas_list(), silent = TRUE)
!inherits(out, "try-error")
}
list_backends <- function() {
if (!has_flexiblas()) {
return(character())
}
flexiblas::flexiblas_list()
}
has_backend <- function(pattern, backends) {
any(grepl(pattern, tolower(backends)))
}
pick_backend <- function(target, backends) {
nm_low <- tolower(backends)
target_low <- tolower(target)
idx <- which(nm_low == target_low)
if (!length(idx) && target_low == "veclib") {
idx <- which(grepl("veclib|vec|apple", nm_low))
}
if (!length(idx) && target_low == "mkl") {
idx <- which(nm_low == "mklopenmp")
if (!length(idx)) {
idx <- which(grepl("mklopenmp", nm_low))
}
if (!length(idx)) {
idx <- which(grepl("mkl", nm_low))
}
}
if (!length(idx) && target_low == "netlib") {
idx <- which(grepl("netlib", nm_low))
}
if (!length(idx)) stop(paste("FlexiBLAS backend not found:", target))
backends[idx[1]]
}
set_backend <- function(backend_name) {
if (!has_flexiblas()) {
return(invisible(NULL))
}
loaded <- flexiblas::flexiblas_list_loaded()
if (!any(tolower(loaded) == tolower(backend_name))) {
flexiblas::flexiblas_load_backend(backend_name)
loaded <- flexiblas::flexiblas_list_loaded()
}
idx <- which(tolower(loaded) == tolower(backend_name))
if (!length(idx)) stop(paste("FlexiBLAS backend not loaded:", backend_name))
flexiblas::flexiblas_switch(idx[1])
}
backend_label <- function(name) {
if (name == "base") {
return("Base")
}
if (grepl("mkl", name, ignore.case = TRUE)) {
return("MKL")
}
if (grepl("netlib", name, ignore.case = TRUE)) {
return("Netlib")
}
if (grepl("veclib|vec|apple", name, ignore.case = TRUE)) {
return("VecLib")
}
name
}
sys <- Sys.info()
arch <- R.version$arch
machine <- sys[["machine"]]
is_mac <- sys[["sysname"]] == "Darwin"
is_arm64 <- grepl("arm64|aarch64", arch) || grepl("arm64|aarch64", machine)
is_intel <- grepl("x86_64|amd64|i386", arch) || grepl("x86_64|amd64|i386", machine)
flex_backends <- list_backends()
use_flexi <- length(flex_backends) > 0
bench_plan <- list()
has_netlib <- use_flexi && has_backend("netlib", flex_backends)
has_mkl <- use_flexi && has_backend("mkl", flex_backends)
has_veclib <- use_flexi && has_backend("veclib|vec|apple", flex_backends)
if (has_netlib && is_intel && has_mkl) {
bench_plan$exact_backends <- c("netlib", "mkl")
bench_plan$rspde_backend <- "netlib"
} else if (has_netlib && is_mac && is_arm64 && has_veclib) {
bench_plan$exact_backends <- c("netlib", "veclib")
bench_plan$rspde_backend <- "netlib"
} else {
bench_plan$exact_backends <- "base"
bench_plan$rspde_backend <- "base"
}
sample_sizes <- c(seq(1000, 10000, by = 1000), 12500, 15000, 20000, 25000, 30000)
sigma_true <- 1.5
range_true <- 0.2
nu_true <- 0.8
sigma_e <- 0.5
kappa_true <- sqrt(8 * nu_true) / range_true
benchmark_data <- lapply(sample_sizes, function(N) {
set.seed(123 + N)
list(
N = N,
locs = matrix(runif(N * 2), ncol = 2),
Y = rnorm(N)
)
})
max_ram_usage <- function(expr) {
start <- gc(verbose = FALSE, reset = TRUE)
eval(substitute(expr), envir = parent.frame())
end <- gc(verbose = FALSE, reset = FALSE)
max_col <- which(colnames(end) == "max used")
if (length(max_col) == 0) stop("gc output does not include 'max used'")
mb_col <- max_col + 1
end["Vcells", mb_col] - start["Vcells", mb_col]
}
run_exact <- function(locs, Y, backend_name) {
if (backend_name != "base") {
set_backend(pick_backend(backend_name, flex_backends))
}
timing_env <- new.env(parent = emptyenv())
timing_env$elapsed <- NA_real_
peak_mb <- max_ram_usage({
Sigma_field <- rSPDE::matern.covariance(
h = as.matrix(dist(locs)),
kappa = kappa_true, nu = nu_true, sigma = sigma_true
)
timing_env$elapsed <- system.time({
loglike_exact_chol(Y, Sigma_field, sigma_e)
})["elapsed"]
})
list(elapsed_sec = as.numeric(timing_env$elapsed), peak_ram = peak_mb)
}
run_rspde <- function(locs, Y, backend_name, m) {
if (backend_name != "base") {
set_backend(pick_backend(backend_name, flex_backends))
}
timing_env <- new.env(parent = emptyenv())
timing_env$elapsed <- NA_real_
peak_mb <- max_ram_usage({
mesh <- fm_mesh_2d(loc = locs, cutoff = 0.0025)
A <- fm_basis(mesh, locs)
obj <- matern.operators(
mesh = mesh, nu = nu_true, range = range_true, sigma = sigma_true,
m = m, parameterization = "matern"
)
timing_env$elapsed <- system.time({
rSPDE:::rSPDE.matern.loglike(object = obj, Y = Y, A = A, sigma.e = sigma_e)
})["elapsed"]
})
list(elapsed_sec = as.numeric(timing_env$elapsed), peak_ram = peak_mb)
}
bench_rows <- list()
for (bm in benchmark_data) {
N <- bm$N
locs <- bm$locs
Y <- bm$Y
for (backend_name in bench_plan$exact_backends) {
if (backend_name == "netlib" && N > 8000) next
exact_vec <- run_exact(locs, Y, backend_name)
bench_rows[[length(bench_rows) + 1]] <- data.frame(
N = N,
backend = backend_label(backend_name),
method = "Exact",
elapsed_sec = exact_vec$elapsed_sec,
peak_ram = exact_vec$peak_ram
)
}
for (m in 1:4) {
rspde_runs <- lapply(seq_len(10), function(i) run_rspde(locs, Y, bench_plan$rspde_backend, m))
rspde_elapsed <- vapply(rspde_runs, function(x) x$elapsed_sec, numeric(1))
rspde_peak <- vapply(rspde_runs, function(x) x$peak_ram, numeric(1))
rspde_net <- list(elapsed_sec = mean(rspde_elapsed), peak_ram = mean(rspde_peak))
bench_rows[[length(bench_rows) + 1]] <- data.frame(
N = N,
backend = backend_label(bench_plan$rspde_backend),
method = paste0("rSPDE m=", m),
elapsed_sec = rspde_net$elapsed_sec,
peak_ram = rspde_net$peak_ram
)
}
}
bench_df <- bind_rows(bench_rows)
results_all <- bench_df %>% mutate(expr = method, median = elapsed_sec)
mem_df <- bench_df %>% mutate(method = method)
if (!"ram_gib" %in% names(mem_df) && "peak_ram" %in% names(mem_df)) {
divisor <- if (max(mem_df$peak_ram, na.rm = TRUE) > 1e4) 1e5 else 1024
mem_df$ram_gib <- mem_df$peak_ram / divisor
}
dir.create("cache", showWarnings = FALSE, recursive = TRUE)
saveRDS(list(results_all = results_all, mem_df = mem_df, sample_sizes = sample_sizes),
file = "cache/timing_benchmark_results.rds"
)